Do you have knowledge of 3-axis VS 5-axis CNC machines? They are the most commonly used CNC machines. In the world of modern manufacturing, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines play a pivotal role in producing precise and complex parts. Each type has its unique advantages and applications, making them suitable for different manufacturing needs. In this article, we will delve into the key differences between 5-axis and 3-axis CNC machines, exploring their capabilities, benefits, and ideal use cases. By understanding the distinctions between these two types of machines, manufacturers can make informed decisions to optimize their production processes.
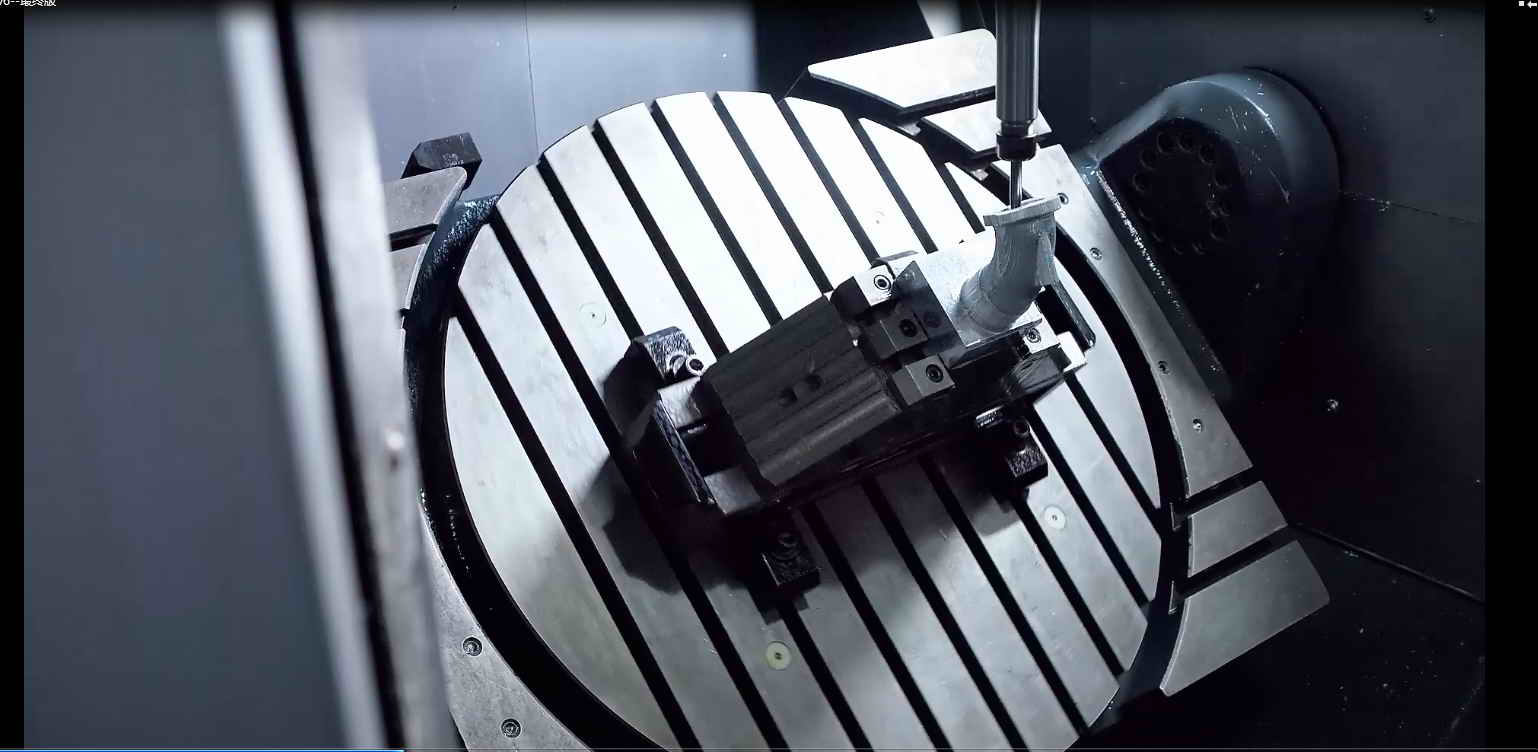

What is a 3-Axis CNC Machine?
Definition and Functionality
A 3-axis CNC machine operates along three primary axes: X, Y, and Z. These machines are capable of moving the cutting tool along these three linear axes to shape and cut the workpiece. The X-axis typically represents left-to-right movement, the Y-axis represents front-to-back movement, and the Z-axis represents up-and-down movement.
Applications
3-axis CNC machines are widely used in various industries for tasks that require straightforward cutting and shaping. Common applications include:
- Milling: Creating flat surfaces, slots, and holes in a workpiece.
- Drilling: Producing precise holes in materials.
- Engraving: Adding detailed designs and text to surfaces.
- Prototyping: Rapidly creating prototypes for testing and validation.
Advantages
- Simplicity: 3-axis CNC machines are easier to program and operate, making them suitable for beginners and straightforward tasks.
- Cost-Effectiveness: These machines are generally more affordable than their 5-axis counterparts, making them a cost-effective solution for many applications.
- Versatility: While simpler, 3-axis machines can handle a wide range of materials and tasks, making them versatile for various industries.
What is a 5-Axis CNC Machine?
Definition and Functionality
A 5-axis CNC machine adds two additional rotational axes to the traditional X, Y, and Z axes, allowing for more complex and intricate machining. These additional axes are typically referred to as the A-axis (rotating around the X-axis) and the B-axis (rotating around the Y-axis). This advanced capability enables the cutting tool to approach the workpiece from virtually any direction.
Applications
5-axis CNC machines are used in industries that require high precision and the ability to create complex geometries. Common applications include:
- Aerospace: Manufacturing turbine blades, engine components, and structural elements.
- Automotive: Producing complex engine parts, custom components, and prototypes.
- Medical: Creating orthopedic implants, surgical instruments, and dental prosthetics.
- Defense: Fabricating weapon systems, vehicle armor, and aerospace defense components.
Advantages
- Enhanced Precision: The additional axes allow for more precise and intricate machining, making 5-axis machines ideal for complex parts with tight tolerances.
- Improved Surface Finish: The ability to maintain a constant angle relative to the workpiece results in a superior surface finish and reduced need for secondary finishing operations.
- Reduced Setup Time: 5-axis machines can machine multiple sides of a part in a single setup, reducing the need for manual repositioning and increasing efficiency.
- Versatility: These machines can handle more complex geometries and intricate details, making them suitable for a wider range of applications.
Key Differences: 5-Axis VS 3-Axis CNC Machines
1. Number of Axes
- 3 Axis CNC Machines: Operate along three linear axes (X, Y, and Z).
- 5 Axis CNC Machines: Operate along three linear axes (X, Y, and Z) and two additional rotational axes (A and B).
2. Complexity and Precision
- 3 Axis CNC Machines: Suitable for simpler tasks that require less precision and complexity.
- 5 Axis CNC Machines: Ideal for complex and intricate parts that demand high precision and tight tolerances.
3. Setup and Operation
- 3 Axis CNC Machines: Typically require multiple setups and manual repositioning of the workpiece for complex parts.
- 5 Axis CNC Machines: Can machine multiple sides of a part in a single setup, reducing setup time and increasing efficiency.
4. Cost
- 3 Axis CNC Machines: Generally more affordable and cost-effective for straightforward tasks.
- 5 Axis CNC Machines: Higher initial cost but offer greater versatility and efficiency for complex applications.
5. Applications
- 3 Axis CNC Machines: Commonly used for milling, drilling, engraving, and prototyping in various industries.
- 5 Axis CNC Machines: Widely used in aerospace, automotive, medical, and defense industries for producing complex and high-precision components.
How to choose: 5-Axis VS 3-Axis CNC Machines
Factors to Consider
When deciding between a 5-axis and a 3-axis CNC machine, several factors should be considered:
- Complexity of Parts: If your production involves complex geometries and intricate details, a 5-axis CNC machine is the better choice. For simpler tasks, a 3-axis machine may suffice.
- Precision Requirements: High-precision applications, such as those in aerospace and medical industries, benefit from the enhanced accuracy of 5-axis CNC machines.
- Budget: Consider your budget and the cost-effectiveness of each machine type. While 5-axis machines have a higher initial cost, their efficiency and versatility may justify the investment for complex applications.
- Production Volume: For high-volume production of complex parts, the reduced setup time and increased efficiency of 5-axis CNC machines can lead to significant cost savings.
- Skill Level: 3-axis CNC machines are easier to program and operate, making them suitable for beginners and simpler tasks. 5-axis machines require more advanced programming skills and expertise.
Industry-Specific Considerations
- Aerospace and Defense: The high precision and ability to create complex geometries make 5-axis CNC machines the preferred choice.
- Automotive: Both 3-axis and 5-axis CNC machines are used, depending on the complexity of the parts and the level of customization required.
- Medical: The need for precision and custom implants makes 5-axis CNC machines ideal for medical applications.
- General Manufacturing: 3-axis CNC machines are widely used for general manufacturing tasks, while 5-axis machines are employed for more complex projects.
Conclusion
The choice between 5-axis and 3-axis CNC machines depends on the specific needs of your manufacturing process. While 3-axis CNC machines are cost-effective and suitable for simpler tasks, 5-axis CNC machines offer enhanced precision, versatility, and efficiency for complex applications. By understanding the key differences and considering factors such as complexity, precision, budget, and production volume, manufacturers can make informed decisions to optimize their production processes and achieve high-quality results. Whether you’re in aerospace, automotive, medical, or general manufacturing, selecting the right CNC machine is crucial for meeting your production goals and staying competitive in the market.